The great explorer of the truth, the master-builder of human happiness no one rejects dislikes avoids pleasure itself because it is pleasure but because know who do not those how to pursue pleasures rationally encounter consequences that are extremely painful desires to obtain.
Read MoreHow the Gig Economy Shapes the Recruitment Market in San Francisco
San Francisco, known for its innovation and vibrant economy, presents unique challenges for gig workers trying to make ends meet. The high cost of living, driven by soaring rental prices, puts immense pressure on these workers. As these workers navigate a city known for its tech-driven opportunities, they face the dual pressures of managing irregular incomes and coping with one of the highest living costs in the country.
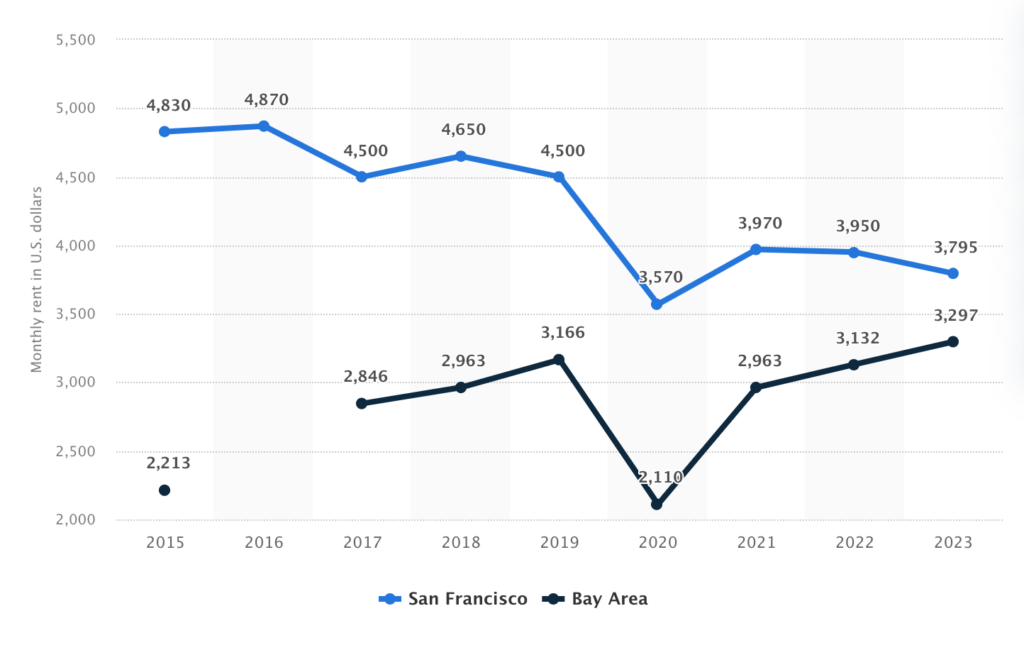
As of 2024, San Francisco is one of the US cities with the highest rental fees. The monthly rent for two-bedroom apartments in San Francisco and Bay Area has fluctuated since 2015. In 2023, the median monthly rent for a two-bedroom apartment in San Francisco was 3,795 U.S. dollars, down from 3,970 U.S. dollars in 2021.
Chart Source: Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1016818/two-bedroom-apartment-rent-san-francisco-bay-area/
Understanding the Gig Economy in San Francisco
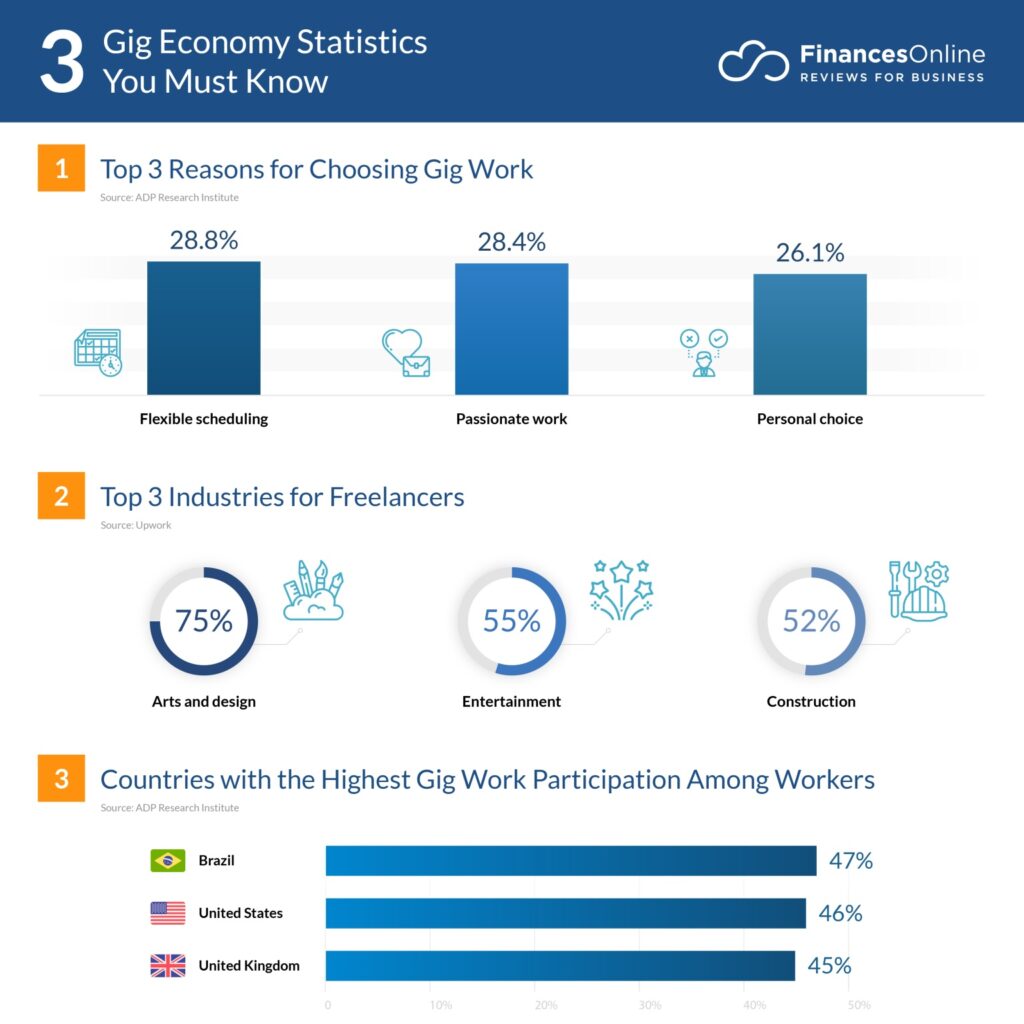
The gig economy in the United States refers to a labor market characterized by short-term contracts or freelance work, as opposed to permanent jobs. This trend has been driven by the rise of digital platforms that connect workers with consumers, such as Uber, Lyft, DoorDash, and freelance websites like Upwork. In San Francisco, the gig economy is a significant part of the city’s workforce, with approximately 36% of workers engaged in various gig roles such as ride-sharing, food delivery, freelance tech work, and creative gigs.
Source: https://wifitalents.com/statistic/gig-economy/#
Key Features of the Gig Economy in San Francisco
One of the defining features of the gig economy in San Francisco is the high degree of flexibility it offers to workers. Gig jobs allow individuals to choose their own working hours, making it easier for them to balance multiple jobs or personal commitments. This flexibility is especially appealing in a city known for its fast-paced lifestyle and high cost of living, as it provides workers with the opportunity to maximize their earnings by working during peak demand times.
However, this flexibility comes with significant trade-offs. Gig workers in San Francisco often face a lack of job security and benefits, which are typically associated with traditional employment. Unlike full-time employees, gig workers are usually classified as independent contractors, meaning they do not receive health insurance, retirement benefits, or paid leave. This classification leaves many gig workers vulnerable, as they must cover these expenses out of pocket, further straining their finances in an already expensive city.
Income variability is another major challenge for gig workers in San Francisco. Earnings can fluctuate widely depending on factors such as time of day, demand for services, and competition from other gig workers. For example, a driver for a ride-sharing service might earn significantly more during major events or rush hours but could see their income drop during off-peak times. This unpredictability makes it difficult for gig workers to plan their finances and achieve financial stability.
Image Source: https://financesonline.com/gig-economy-statistics/
Survival Strategies for Gig Workers
The already tough conditions for gig workers in San Francisco are made even harder by the high cost of living. With median rents hits almost $4,000 per month, many gig workers struggle to afford housing and basic necessities. To cope with these high costs, many gig workers in San Francisco adopt shared housing and co-living. By splitting rent and utilities, these living arrangements make it more affordable to live in the city. Co-living spaces specifically designed for gig workers offer flexible and lower-cost living options, which are essential in managing expenses in an expensive urban environment.
Financial management and planning are crucial for gig workers dealing with irregular income. Many use budgeting apps and financial planning tools like Mint and YNAB (You Need A Budget) to track their earnings and expenses. Non-profits and community organizations provide financial advice and resources, helping gig workers better manage their finances and save for unexpected expenses.
To maximize their earnings, many gig workers diversify their income streams by taking on multiple roles. For instance, combining ride-sharing with food delivery or freelance work helps them stabilize their income. By leveraging platforms that offer higher pay rates and more consistent work opportunities, gig workers can better manage their finances and reduce the impact of income fluctuations.
The Implications of the Gig Economy on the Recruitment Market in the US
| Aspect | Implications for Employers | Implications for Job Seekers |
| Increased Flexibility and Adaptability | The gig economy allows companies to adjust their workforce based on demand, providing greater flexibility in managing labor costs. Employers can hire gig workers for short-term projects, reducing the need for long-term commitments and fixed payroll expenses. | Gig work offers job seekers increased flexibility, enabling them to manage their schedules and pursue multiple opportunities simultaneously, which is particularly beneficial for those prioritizing work-life balance. |
| Shift in Recruitment Strategies | Recruitment strategies must adapt to attract gig workers, focusing on digital platforms and social media where these workers are active. Traditional recruitment methods may be less effective for reaching gig workers who rely on apps and online platforms to find job opportunities. | Gig workers need strong online profiles and portfolios to stand out in a competitive market. Effective self-marketing on gig platforms and social media is crucial for attracting potential employers and securing work. |
| Changes in Skill Requirements | The gig economy emphasizes specialized skills. Employers often seek workers with specific expertise for short-term projects, leading to a demand for niche skills and encouraging the hiring of highly skilled freelancers rather than generalists. | Gig workers must continuously update and diversify their skill sets to remain competitive. Lifelong learning and professional development become essential as gig workers adapt to the evolving demands of the market. |
| Impact on Employment Benefits | Hiring gig workers can reduce the burden of providing traditional employment benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, resulting in significant cost savings. However, this also raises ethical and legal considerations regarding worker welfare and protection. | Gig workers often lack access to traditional employment benefits, leading to financial insecurity and challenges in securing health insurance, retirement savings, and other essential benefits. This situation has sparked discussions about the need for new models of worker protection and benefits tailored to the gig economy. |
| Influence on Workforce Demographics | The gig economy can help diversify the workforce by providing opportunities for individuals from various backgrounds, including those who may face barriers to traditional employment, such as people with disabilities, caregivers, and those in rural areas who can work remotely. | The gig economy offers alternative employment opportunities to individuals who might struggle to find traditional jobs, such as recent graduates, retirees, and those with unconventional career paths. It provides a platform for these individuals to leverage their skills and talents in new ways. |

The gig economy in San Francisco’s high-rent market highlights both the resilience and resourcefulness required by gig workers to thrive amidst challenging conditions. As gig work continues to shape the employment landscape, understanding its impact on recruitment strategies and employment benefits is crucial. While gig workers enjoy greater flexibility and the ability to manage multiple opportunities, they also face the challenge of securing essential benefits and maintaining competitive skills. Employers, in turn, must adapt their strategies to attract and retain specialized talent in a rapidly evolving market. Understanding these dynamics helps everyone navigate the gig economy more effectively, leading to better outcomes in the job market.
For more insights into the US recruitment market, contact us at:
O: +1 (801) 609-4008 | M: +1 (415) 730-8827 | E: bill.armstrong@praxt.com | W: www.praxt.com



